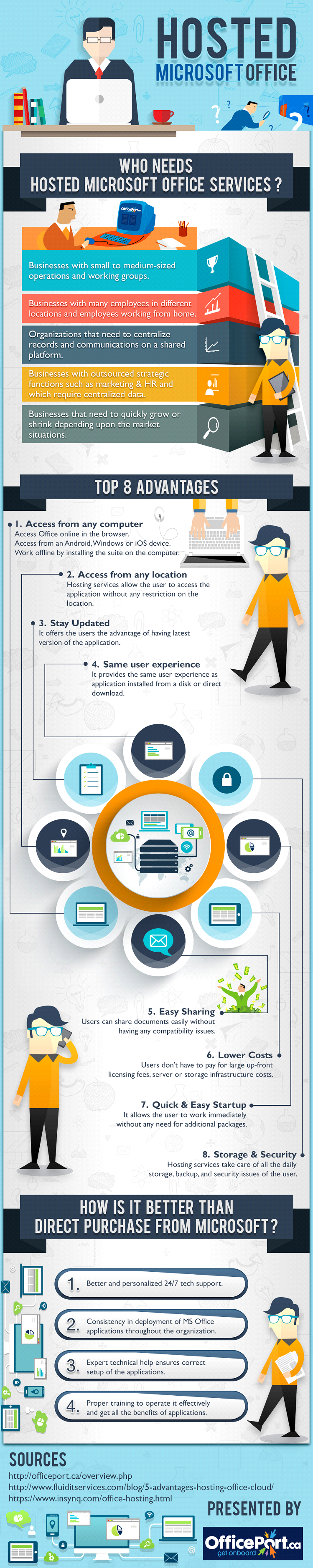
Hosted computing means that your Microsoft Office 365 applications or software, data, and computing needs are accessed, stored, and occur over the Internet or the cloud.
Companies would pay a monthly fee, per user, only for those services they used delivered via the Internet. The idea was to host the software on a website and for it to be available to companies anytime, anywhere.
By using the Internet as the delivery platform, an on-demand service in an infrastructure gave customers the ability to use software fully managed not by their own IT department but by their cloud service provider.
For most small businesses, this type of deployment model is referred to as the “public cloud” where the cloud computing service is owned by a provider offering the highest level of efficiency. For organizations where a “one-size-fits-all” approach doesn’t work, two other deployment models for cloud computing are available: private clouds and hybrid clouds.
A private cloud is typically dedicated to one organization on its own highly secure, private network. A hybrid cloud is simply a combination of the public and private clouds. As an example, applications in a hybrid cloud may be run in a public cloud but customer information is stored in a database in a private cloud.
Regardless of the deployment model used, cloud computing means that your business applications are outsourced somewhere on the Internet where you don’t have to worry about paying for capacity you don’t need. It also means that the version of the software you’re using is always the latest version; it is accessible anytime, anywhere.